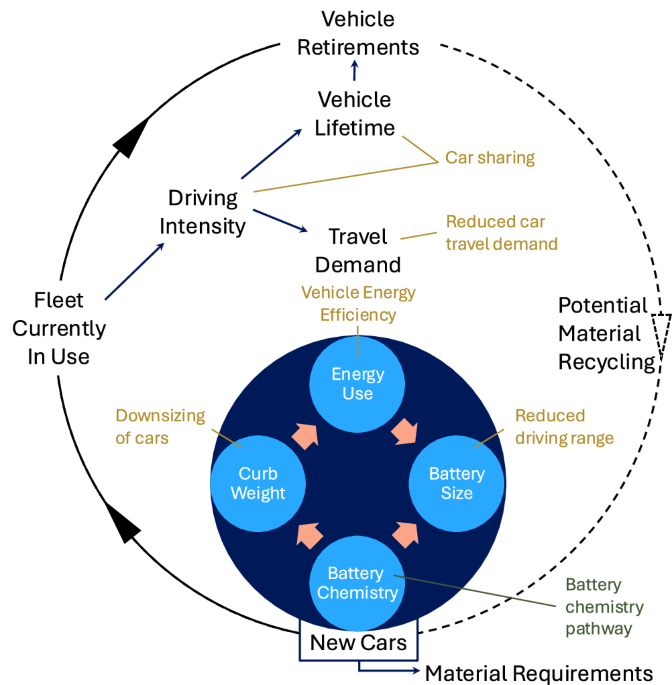
The components that affect battery materials demand for electrical vehicles are associated to a number of interlinked methods. On this research, we concentrate on the automobile and fleet methods whereas the fabric necessities for a sure battery chemistry are primarily based on earlier analysis. Therefore, we think about two battery chemistry pathways that develop individually from the opposite measures that we analyze. The fabric demand of the entire fleet is pushed by the variety of new vehicles manufactured in a sure 12 months and the scale of the battery in these vehicles, see Fig. 1. The variety of vehicles wanted depends upon the automobile lifetime of the vehicles within the present fleet and the journey exercise every automotive can provide every year (i.e., the driving depth). The driving depth is increased for a shared automotive, however on the similar time, the automobile lifetime is shorter as a result of automotive being extra intensely used29. Lastly, the fleet serves to meet a given journey demand per 12 months. The battery dimension for a given driving vary is decided by the scale of the automotive, which impacts the mass in working order and, in flip, the particular vitality use of the automotive. On the similar time, the assumed battery chemistry influences the gravimetric vitality density of the battery, that means {that a} battery with a decrease vitality density would result in an elevated mass in working order for a given driving vary. The interaction between these components is absolutely represented within the mannequin, see particulars in “Strategies”.
Be aware that the dashed line in Fig. 1 represents the quantity of supplies remaining in autos reaching end-of-life, setting a theoretical most potential for recycling. There are limits to how environment friendly such methods might be, and we acknowledge that recycling with out losses is unattainable. After quantifying the full cumulative materials necessities, the theoretical most recycling potential is introduced for every state of affairs indicated as a decrease sure for cumulative materials necessities from virgin sources.
The state of affairs evaluation compares completely different measures for diminished materials demand with a reference state of affairs for every of the battery chemistry pathways, each if applied in isolation and if all measures are mixed in a low materials demand state of affairs. The principle assumptions for every measure are summarized in Desk 1. All measures are launched linearly from 2022 and attain 100% of the market by 2040, apart from automotive sharing which follows a Gompertz-curve reaching 98% of the market by 2050. Particular parameters for the overall assumptions, the reference state of affairs, and the low materials demand measures are offered in Supplementary Tables 1, 2, and three, respectively. The estimated particular vitality use per pushed km, the mass in working order, and the battery dimension for every measure, in addition to for the reference and low materials demand eventualities, are offered in Supplementary Desk 5.
The evolution of cathode chemistries has been pushed by uncooked materials prices in addition to efficiency and additional developments are expected42. Shifts in the direction of chemistries with excessive nickel content material, together with Nickel Cobalt Aluminum-oxide (NCA) and completely different combos of Nickel, Manganese, and Cobalt (NMC), have been noticed over the past decade10. Larger nickel content material within the cathode usually implies increased storage capability however a shorter cycle life and decrease thermal stability, whereas Lithium Iron Phosphate (LFP) cathodes have a decrease storage capability however are thought-about extra sturdy when it comes to biking life43. Growing uncooked materials prices triggered a halt within the lowering prices of Li-ion battery cell manufacturing in 2022 and affected battery choices44. Whereas there have been technological advances in solid-state batteries, different anode chemistries, and their respective electrolytes, such improvements face challenges when scaling up when it comes to manufacturing processes in addition to reaching a sturdy provide chain42. Therefore, we assume that short- to medium-term battery markets will probably be dominated by current battery designs.
The battery chemistries used within the base 12 months (2022) are assumed to be consistent with the common in European gross sales of recent vehicles (primarily based on market shares of LFP, low-nickel, and high-nickel content material batteries in European sales44 and the worldwide market shares of particular battery chemistries throughout the low-nickel and high-nickel content material categories45). The ensuing market shares within the base 12 months are 19% NMC111, 32% NMC622, 35% NMC811, 11% NCA, and three% LFP. The 2 pathways begin from the bottom 12 months and comply with linear trajectories to succeed in 100% of the market by 2040 for high-nickel content material batteries (i.e., NMC811) and cobalt- and nickel-free batteries (illustrated by LFP in our evaluation), respectively.
The assumed battery chemistry impacts materials demand per kWh10, see Supplementary Desk 4, and the gravimetric vitality density of the battery46, see Supplementary Desk 1, which impacts the automotive’s mass in working order for a given battery capability. Additional, the volumetric vitality density additionally differs between completely different battery applied sciences. In our eventualities, we assume that the doubtless bigger battery pack quantity wanted for an LFP battery as in comparison with an NMC battery, when assuming the identical vary, comes on the expense of a smaller cabin and/or trunk quantity. Therefore, the assumed battery chemistry leaves different features of the automobile design traits intact (e.g. frontal space, aerodynamics, glider, and drivetrain mass). Be aware additionally that we assume the battery lifetime to be equal to the automobile lifetime and that each are negatively affected by the upper annual driving depth assumed for shared cars29.
The precise vitality utilized in an electrical automotive depends upon (i) the automotive’s whole mass, (ii) the automotive’s frontal space and the aerodynamic drag, (iii) the rolling resistance, (iv) the vitality recovered via regenerative braking, (v) powertrain losses, and (vi) the extra vitality use wanted to energy cabin heating/cooling, infotainment methods, and the driving behavior20,21. The common particular vitality use in 2022 was 220 W h km-1, primarily based on producers’ data47 for electrical vehicles offered in Sweden. The precise vitality use has been adjusted for 25% increased vitality use to account for real-world driving situations. This may be in comparison with a 19% discrepancy between measured particular vitality use and declared particular vitality use primarily based on the WLTP for BEVs used within the Netherlands48. We assume a barely increased discrepancy as a result of colder climate situations in Sweden, which requires bigger ranges of vitality use for reaching an appropriate degree of thermal consolation within the cabin.
We use a model20,21 following the worldwide harmonized mild automobile testing cycle (WLTC) to estimate the vitality use per km for future vehicles, together with the affect of vitality effectivity measures. Automobile design has a notable affect on aerodynamic drag; for instance, the drag might be diminished by redesigning the form of the tail part and rounding the nostril of the car49. Reductions in rolling resistance—via bigger rim sizes, shallower thread depth, and decrease velocity scores—might end in a 40% lower within the rolling resistance coefficient50,51. Regenerative braking additionally contributes to lowering the general vitality use and depends upon the route, the capability of the drivetrain, and the charging/discharging efficiencies of the battery20,21. Be aware that the assumed 25% adjustment to account for real-world driving situations implies giant reductions in vitality use for heating/cooling within the low materials demand state of affairs when the vitality use for propulsion is diminished. For instance, warmth pumps, and different new heating applied sciences, can scale back energy demand for cabin heating20,52,53, however reaching the implied discount will doubtless require extra measures, reminiscent of localized heating20 and improved insulation54,55.
The dimensions of each standard and electrical vehicles has been growing globally44. The common mass in working order of recent vehicles in Sweden has elevated from 1566 kg in 2014 to 1834 kg in 2022, see Supplementary Fig. 1. Whereas this pattern might be partly defined by a shift in the direction of electrical vehicles and plug-in hybrid electrical vehicles, the same pattern can also be proven for the person vehicles with completely different drivetrains, see Supplementary Fig. 1, confirming a pattern in the direction of heavier vehicles that dates again not less than to the 1970s56. Lowering the mass in working order might be a measure to scale back materials demand because the mass in working order impacts the particular vitality use and, therefore, the battery capability required for a given driving vary. Lowered common mass in working order might be achieved via light-weight supplies within the automobile design57 and by customers shopping for smaller cars58. A number of methods for utilizing light-weight supplies are already obtainable—a pattern not solely pushed by sustainability efforts but additionally by prices and efficiency with out compromising structural safety59.
We assume a discount in glider mass of 15% on account of light-weight supplies already within the reference scenario20, reaching a median glider mass of 1275 kg (i.e., the mass of the physique and chassis, excl. engine, drivetrain, and battery). As low materials demand measures, we think about the mixed impact of diminished automobile dimension, from giant autos on common to decrease medium20, and diminished glider mass of 25% on account of light-weight materials20,60, leading to a mass of 863 kg. The decrease medium automobile dimension is also assumed to have a smaller frontal space, 2.2 m2 in comparison with 2.4 m2 for the massive car20, which contributes to diminished drag and decrease particular vitality use.
The mannequin additionally accounts for the added mass of the battery in response to the assumed vary and the analyzed battery chemistry because the gravimetric vitality density varies between battery chemistries.
Inadequate vary is seen as an impediment to electrical automotive adoption and is probably going associated to psychological factors61. Therefore, tailoring charging to the consumer’s journey patterns might reveal a possible discount in battery sizes. The common driving vary in 2022 for brand new electrical vehicles offered in Sweden was 355 km (adjusted with 25% increased vitality use to account for real-world driving situations)47. We assume that vehicles with excessive engine energy can be utilized as a proxy for a luxurious market phase and obtainable statistics present that there isn’t any marginal enhance in vary with growing engine energy above a sure degree, see Supplementary Fig. 2. A driving vary of 400 km aligns with the common driving vary of recent electrical vehicles offered in Sweden in 2022 with a better engine energy than 200 kW and better mass in working order than 1800 kg. Therefore, we assume that the demand for additional vary saturates at 400 km within the reference state of affairs.
The necessity for giant battery sizes might be restricted by dense entry to quick chargers alongside main highways27 or applied sciences for charging whereas driving, reminiscent of inductive charging on electrical roads26 or, probably, wired peer-to-peer charging62. As a low materials demand measure, we assume that the driving vary might be halved, which is consistent with the affect of implementing electrical roads on 25% of nationwide and European roads in Sweden (eq. to round 4000 km)26 or of dense entry to quick chargers alongside main highways, primarily based on outcomes for Seattle27. This assumption must be seen as a proxy for a future growth the place demand for battery capability is diminished by a large-scale enlargement of quick charging and/or electrical roads that make it attainable for customers to attain their journeys with out worrying about their driving vary and the place the quick charging or charging whereas driving doesn’t result in main battery degradation. The assumed driving vary not solely impacts the battery dimension but additionally the particular vitality use and the mass in working order of the automotive as a result of discount in battery capability wanted.
The Swedish automotive fleet, with 5.8 million vehicles in 2022, has traditionally been dominated by vehicles owned or leased by individuals63. The introduction of related and autonomous vehicles might allow each the sharing of vehicles and rides, the place they’ll scale back the required fleet dimension wanted to produce a given journey demand64. Nevertheless, shared vehicles could be pushed extra intensely, which might end in shortening their lifetime within the fleet29. As a low materials demand measure, we assume {that a} shared autonomous automotive might change 5 individually held vehicles, which is in line with a simulation research on automobile sharing in Gothenburg65. We assume that sharing will ultimately be absolutely adopted in bigger cities, municipalities inside commuting distance of bigger cities, and medium-sized cities. We don’t think about automotive sharing to be an choice within the reference state of affairs.
Demand per capita for passenger automotive journey in Sweden has been comparatively secure over the past 20 years, see Supplementary Fig. 3. Nonetheless, the Swedish Transportation Administration66 initiatives a 21% enhance within the annual journey demand by passenger automotive per capita in 2050 in comparison with the 2022 degree. Nevertheless, measures reminiscent of improved public transport methods, teleworking32, and societal life-style developments might scale back the demand for passenger automotive travel33. Strolling, biking, and public transport can change passenger vehicles and scale back automotive journey demand by as much as 10%, distant teleworking two days every week for half the individuals who commute can lower the demand for automotive journey by one other 5%, and, as well as, some longer leisure journeys might be shifted to long-distance public transport choices or absolutely omitted leading to automotive journey demand reductions of as much as 9percent35. These adjustments might happen on account of life-style adjustments and/or elevated price of automotive utilization, for instance, on account of km-taxes, excessive battery costs, and/or excessive electrical energy prices35.
We assume that journey demand by passenger automotive follows governmental projections within the reference state of affairs. As a low materials demand measure, we think about a discount in journey demand by passenger automotive per capita by 21% in 2050 in comparison with the 2022 degree. Such a discount in journey demand is giant however on par with the Swedish Transport Administration’s low passenger automotive demand pathway66. Whereas this measure is assumed to extend demand for public transport, buses particularly, Sweden reveals a notably low occupancy fee for buses, which signifies a possible for elevated bus journey with out growing bus traffic35.
The cumulative demand, representing the cumulative whole influx of fabric into the electrical automotive fleet for the vary of supplies thought-about within the evaluation, is proven in Fig. 2 and Supplementary Desk 7. The in-use inventory of fabric is the fabric that’s tied up within the Swedish automotive fleet at a given second in time and represents the minimal quantity of fabric that may be required for the fleet, see leads to Fig. 3 and Supplementary Desk 8. The distinction between the cumulative demand and the in-use inventory is the quantity of fabric originating from the Swedish automotive fleet that turns into eligible for recycling. We assume that the share of electrical vehicles in new automotive gross sales will method 100% in 2030, which is consistent with the governmental proposals for speedy electrification of the passenger automotive fleet62,67.
Within the battery chemistry pathway that transitions to NMC811, the cumulative demand and the in-use shares enhance for all metals within the reference state of affairs, except the in-use inventory of manganese and cobalt, and are prone to proceed growing after 2050, see Fig. 2 and Fig. 3. The stagnation and eventual lower of the in-use inventory of manganese and cobalt is a results of the shift to the nickel-rich NMC811. Within the battery chemistry pathway that transitions to LFP, a stagnation in cumulative demand for nickel, manganese, and cobalt is noticed round 2035 following the phase-out of NMC batteries in new gross sales. For this pathway, the in-use inventory subsequently decreases as autos with NMC batteries are retired. This means that the annual demand (influx) for the fabric as enter to new battery manufacturing wanted for the Swedish fleet is smaller than the fabric in vehicles that attain end-of-life (outflow), see Supplementary Figs. 4-6.
By 2030, diminished journey demand has the strongest cumulative demand discount potential (16–17%, relying on materials) adopted by diminished driving vary (14–16%), automobile vitality effectivity (9–10%), automotive sharing (6–7%), and downsizing of vehicles (4–5%), see Supplementary Desk 7. The relative discount potentials are inside these ranges for each battery chemistry pathways. Nevertheless, absolutely the discount is bigger for nickel, manganese, and cobalt within the battery chemistry pathway that transitions to NMC811, whereas the alternative applies to graphite. By 2050, lowering driving vary has the strongest cumulative demand discount potential (36–42%), adopted by diminished journey demand (27–30%), automobile vitality effectivity (25–30%), automotive sharing (18–21%), and downsizing of vehicles (12–14%). Nevertheless, these outcomes don’t apply to nickel, manganese, and cobalt within the battery chemistry pathway that transitions to LFP. For these supplies, the impacts of the measures are notably diminished though the rating stays.
Comparable discount potentials are proven for the in-use inventory by 2030, see Supplementary Desk 8. By 2050, the in-use inventory discount potential of diminished driving vary is as excessive as 47–50% for all supplies within the pathway that transitions to NMC811 in addition to for lithium and graphite within the pathway that transitions to LFP. Automobile sharing is ranked because the second most impactful measure with an in-use inventory discount potential of 36–37%, which is bigger than the discount potential noticed for this measure within the cumulative demand (18–21%). This may be defined by automotive sharing lowering the scale of the fleet however growing the annual journey distance by vehicles used for sharing, which causes a discount within the automobile lifetime, thereby growing the turnover fee. Car vitality effectivity is the third-ranked measure with an in-use inventory discount potential of 33–35%, adopted by diminished journey demand (32–33%) and downsizing of vehicles (16%). For the battery chemistry pathway that transitions to LFP, the discount potentials are barely decrease for nickel, manganese, and cobalt for all measures.
The mixed impacts of all measures within the low materials demand state of affairs present discount potentials by 2030 of 36–40% for the cumulative demand and 34–37% for the in-use inventory. By 2050, the outcomes range relying on the battery chemistry pathway, the place cumulative demand might be diminished by 68–75% and the in-use inventory by 85–87% for all supplies in transition to NMC811 in addition to for lithium and graphite in transition to LFP. For nickel, manganese, and cobalt within the pathway that transitions to LFP, the discount potentials are considerably decrease, the place the cumulative demand might be diminished by 50% and the in-use inventory by 72%.
We analyze our outcomes’ sensitivity to adjustments within the following assumptions: (i) phaseout 12 months of inner combustion engines (primarily based on current EU regulation68), (ii) capability of shared vehicles to switch standard ones, (iii) assumed enhance in particular vitality use to regulate for real-world situations, (iv) automobile vary, (v) implementation 12 months for analyzed measures, and (vi) automotive dimension sooner or later. Particulars on the modified parameters are offered in Supplementary Desk 6. The in-use inventory of supplies in 2050 is probably the most delicate to bigger automotive sizes sooner or later, which applies to all supplies, each battery chemistry pathways, and all eventualities besides the mixed low materials demand state of affairs, see Supplementary Fig. 7. The low materials demand state of affairs, combining the affect of all measures, is mostly much less delicate to those adjustments in assumptions. The implementation 12 months for analyzed measures additionally has a notable affect on the in-use nickel, manganese, and cobalt shares within the pathway that transitions to LFP. The cumulative materials demand till 2050 can also be delicate to bigger automotive sizes sooner or later, resulting in a notable enhance in cumulative demand, in addition to the phaseout 12 months of inner combustion engines, resulting in a notable lower in cumulative demand, see Supplementary Fig. 8. Much like the in-use inventory of supplies, the implementation 12 months for analyzed measures additionally has a notable affect on the in-use nickel, manganese, and cobalt shares within the pathway that transitions to LFP.
Whereas automotive sharing and diminished journey demand have an effect on the scale of the fleet and the way the fleet is used, the remaining measures every have a direct affect on the battery capability of recent autos and have an effect on the interaction between measures. We illustrate this by rating the affect on battery dimension of various combos of measures (Fig. 4). The rating of various measures’ impacts on battery capability exhibits that the person measure with the strongest affect is reductions within the driving vary adopted by vitality effectivity enhancements. The relative impacts of light-weight supplies (−5%) and smaller vehicles (−14%) are the identical for any assumed vary or battery chemistry, whereas absolutely the contribution to lowering battery capability is decrease when the vary requirement is diminished. Together with vitality effectivity, the relative impacts of lightweighting and smaller vehicles are additionally diminished. Be aware that the trade-off in elevated battery capability on account of decrease gravimetric vitality density when switching to the much less material-intense LFP chemistry is comparatively small and will probably be compensated for by implementing light-weight supplies alone.
The cumulative materials necessities till 2050 might be seen as a variety for every state of affairs in addition to for quantifying the affect of every measure when applied in isolation, see Fig. 5. The upper worth within the vary represents the full cumulative demand of uncooked supplies for electrifying the automotive fleet, no matter supply. The decrease worth within the vary, equal to the in-use inventory, is the minimal whole demand for virgin uncooked supplies that may be required even when all materials obtainable from autos that attain end-of-life could be used within the manufacturing of recent vehicles with no or negligible losses. This doesn’t imply that it’s attainable to succeed in 100% recycling effectivity however fairly illustrates that a big influx of uncooked supplies to the Swedish system will inevitably be required.
The leads to Fig. 5 present that the measures to scale back battery materials demand might be as vital as recycling in lowering the fabric necessities till 2050. In actual fact, the cumulative materials demand within the low materials demand state of affairs leads to considerably decrease materials necessities than might even be achieved by excessive ranges of recycling of supplies within the reference state of affairs, apart from nickel, manganese, and cobalt within the battery chemistry pathway that transitions to LFP. In different phrases, all measures mixed can for these supplies obtain notably bigger reductions in demand for virgin uncooked supplies than the portions turning into obtainable for recycling. The truth that recycling processes at all times include losses additional stresses the significance of the low materials demand measures analyzed right here. It’s, nonetheless, vital to level out that the impacts of the measures are much less vital for lowering the demand for nickel, cobalt, and manganese if the battery trade decides to desert the NMC-based battery expertise.
To contextualize our outcomes, we evaluate the cumulative materials necessities to an equal per capita share of the worldwide reserves and sources for every materials, represented by the vertical traces in Fig. 5 and Desk 2 (see Strategies for an outline of how that is calculated). This comparability is beneath the belief that these supplies would solely be used for batteries in passenger vehicles, whereas demand for these supplies additionally exists for different functions which will develop as effectively.
The reference state of affairs is throughout the equal per capita share of the fabric sources for manganese, lithium, and graphite (though barely for graphite within the pathway that transitions to LFP). For cobalt and nickel, the equal per capita share of fabric sources is exceeded within the reference state of affairs for the pathway that transitions to NMC811 and barely exceeded additionally for cobalt for the pathway that transitions to LFP. For the pathway that transitions to NMC811, some measures (i.e., diminished driving vary, diminished automotive journey, and automobile vitality effectivity) can individually scale back the cumulative materials necessities sufficient for nickel, however no measure achieves this for cobalt. With all measures mixed, cumulative materials necessities are inside an equal per capita share of the fabric sources in each battery chemistry pathways and for all assessed supplies. Staying inside an equal per capita share of the reserves is proven to be harder. This degree is exceeded within the reference state of affairs for all supplies besides manganese and nickel within the pathway that transitions to LFP. Combining all measures achieves the required degree or reductions for lithium and graphite, whereas particular person measures fall quick. Nevertheless, for cobalt in each battery chemistry pathways and nickel within the pathway that transitions to NMC811, it is going to be troublesome to remain inside an equal per capita share of the fabric reserves.
We don’t argue that an equal per capita share of a sure reserve or useful resource essentially represents a good distribution of the useful resource and fairly serves as an indicator of the relative use of a sure materials in a rustic in comparison with the obtainable provide. A dialogue on the truthful distribution of those sources shouldn’t be primarily based solely on a per capita allocation however ought to additionally bear in mind sustainability challenges throughout materials provide chains69,70, geopolitical risks71, and the function of markets and property rights72. It is usually vital to notice that estimated world reserves must be seen as a snapshot of present situations and are dynamic over time as sources are transformed to reserves with altering financial and technological circumstances or additional exploration, whereas reserves might additionally change into unusable if Environmental, Social, and Governance dangers are uncovered70.
From a European perspective, lowering the reliance on these supplies might have a big affect on the required imports of major and refined supplies. Solely small fractions of the European demand for these supplies are additionally extracted or refined throughout the European Union, apart from some nickel3. Therefore, lowering demand will doubtless even be vital for lowering dependence on imports in addition to limiting the necessity for brand new mining each inside Europe and in different components of the world.