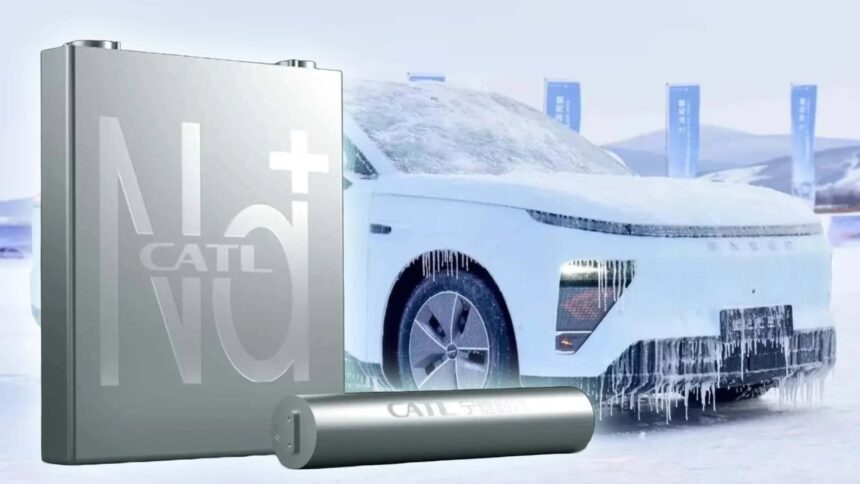
- CATL’s second-generation sodium-ion cells can reportedly discharge usually even at -40 levels Celsius (-40F as temperature scales converge).
- Relying on the make and mannequin, EV batteries carry out the most effective between 60F to 110F. The working vary can go a lot greater or decrease, however that impacts efficiency and vary.
- Sodium-ion battery manufacturing is in its nascent stage, however a number of battery makers, together with BYD, CATL and Northvolt are betting on them for sure low-energy density purposes.
China is reaching new heights in diversifying the battery chemistries utilized in electrical autos. The nation is already main in subcategories of lithium-based chemistries, like nickel-manganese-cobalt (NMC), nickel-aluminum-cobalt (NCA) and lithium-iron-phosphate (LFP). Earlier this 12 months, state-run utility firm China Southern Energy Grid even deployed sodium-ion batteries for stationary power storage. Now CATL, the world’s largest battery maker, claims to have unlocked new ranges of utmost climate efficiency with sodium-ion batteries.
The function of sodium ions is just like lithium ions, the place charge-carrying ions journey between the optimistic and unfavourable electrodes throughout the cost and discharge cycles. Research counsel that sodium-ion batteries may get rid of the pesky traits of lithium-ions: There’s much less danger of thermal runaway, they will function at diversified temperatures and crucially, the price of sodium hydroxide, a key uncooked materials, is way decrease than lithium-hydroxide. (Though battery corporations have reached higher economies of scale with lithium-ions.)
Sodium-ion batteries have already entered manufacturing in China. Automobiles that use them embody the Yiwei EV produced by Volkswagen-backed JAC and the JMEV EV3. Talking on the World Younger Scientists Summit, CATL chief scientist Wu Kai stated that its second-generation sodium-ion cells can discharge usually even at -40 levels Celsius, as per a number of native Chinese language media reviews. Which means EVs with such batteries will not lose vary underneath frigid temperatures, which may assist tackle a few of the lingering issues relating to the acute climate efficiency of batteries. They are going to launch in 2025 in China, with mass manufacturing anticipated to start in 2027.
Excessive warmth and excessive chilly are each enemies of a lithium-ion battery. In excessive chilly, chemical processes inside a cell decelerate, as lithium-ions cannot transfer as freely as they will underneath regular temperatures. Much like how water struggles to movement by means of frozen pipes, electrical power in a chilly battery faces extra resistance. This results in decrease driving vary, longer charging instances and extended publicity to excessive temperatures may even impression long-term battery well being. At the very least in concept, sodium ions resolve this drawback as they’re much more resilient.
Photograph by: CATL
Tesla’s 4680 NCM cells in some newer Mannequin Ys have an estimated power density of as much as 296 watt-hours per kilogram, as per some early teardowns. Sodium-ion batteries are much less energy-dense. Whereas CATL has not disclosed the power density of the brand new cells, it reportedly goals to succeed in a determine of 200 Wh/kg—a tricky aim on condition that even LFP batteries have solely not too long ago hit that mark. That might solely be applicable for low-range EVs or entry-level trims. Some reviews additionally declare sodium-ion batteries are anticipated to exchange 20-30% of LFP batteries in choose purposes.
A examine revealed within the U.S. authorities’s Nationwide Library of Medication calls sodium-ion batteries a “rising star.” Battery giants like CATL, BYD, and Sweden’s Northvolt are already investing in and creating these next-generation cells. So both method, one factor is evident: the way forward for battery chemistry isn’t headed in a single route however will seemingly embrace a mixture of chemistries tailor-made to particular use instances.
Contact the writer: suvrat.kothari@insideevs.com